When it comes to electrical installations, choosing the right connector is essential to ensure a safe and efficient system. Several factors should be considered when selecting an electrical connector including the material, cross-section and diameter of the conductor, the type of cable and the effects of galvanic corrosion.
This article will explore the importance of choosing a good electrical connector and look at the differences between using copper or aluminium, the impact of cable type and the phenomenon of galvanic corrosion. We will also discuss the advantages of bimetallic connectors and explain the key conclusions.

The material
The material used for the electrical connector is a crucial aspect that affects the performance and durability of a system. Copper and aluminium are both widely used in the electrical industry. Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. It is ideal for grounding and power distribution applications. Aluminium, on the other hand, is lighter and less expensive than copper but it has lower electrical conductivity. It is widely used in overhead power transmission installations because of its weight (it is 70% lighter than copper with the same cable cross-section). The choice of material depends on the specific needs of the installation, with factors such as the current capacity required and budget being taken into account.
Diameter of the cable
Another important aspect to consider is the diameter of the cable. The diameter of copper conductors is not the same as that of aluminium conductors for the same cross-section, especially when using flexible copper cable. This is one of the main reasons why the same bimetallic connector cannot be used for both copper and aluminium cables. Indeed, the concept “bimetallic”, when used for a terminal, means that it is used to connect Al wires to Cu plates or the other way around. Remember that in order to select the appropriate connector according to the type of cable used, the recommendations and technical specifications must be consulted.
Galvanic corrosion
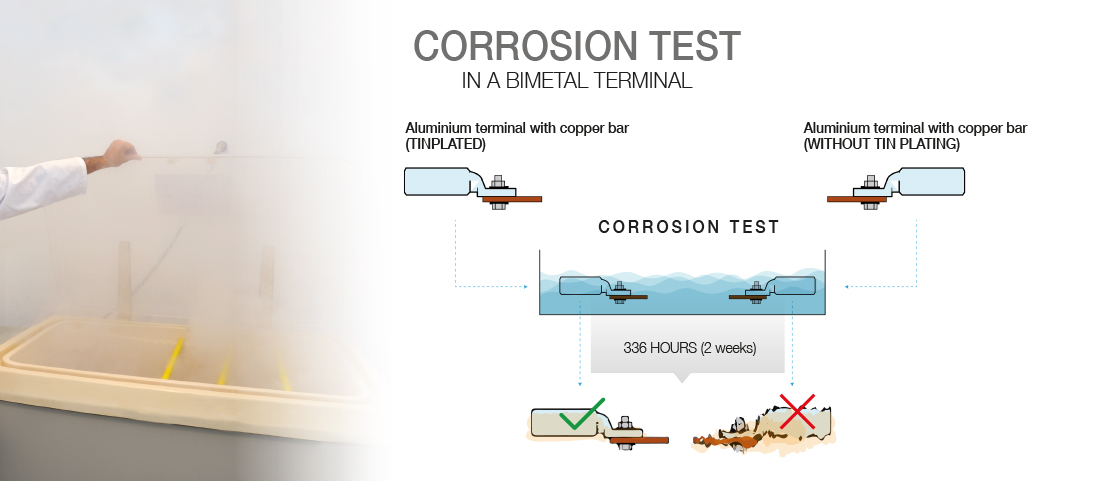
Galvanic corrosion is a phenomenon that occurs when two different metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte, e.g. moisture from condensation. This can lead to degradation of connectors and negatively affect their performance. Galvanic corrosion is particularly relevant when using materials that have very different electrode potentials, such as copper and aluminium. To avoid this problem, it is advisable to use connectors that are specifically designed to resist galvanic corrosion, such as bimetallic connectors. These connectors combine materials such as copper and aluminium in a special construction or have a layer of tin that acts as an “intermediary” between the two metals, thus minimising the effects of galvanic corrosion. In addition, they offer greater durability and longer life compared to conventional connectors.
 |
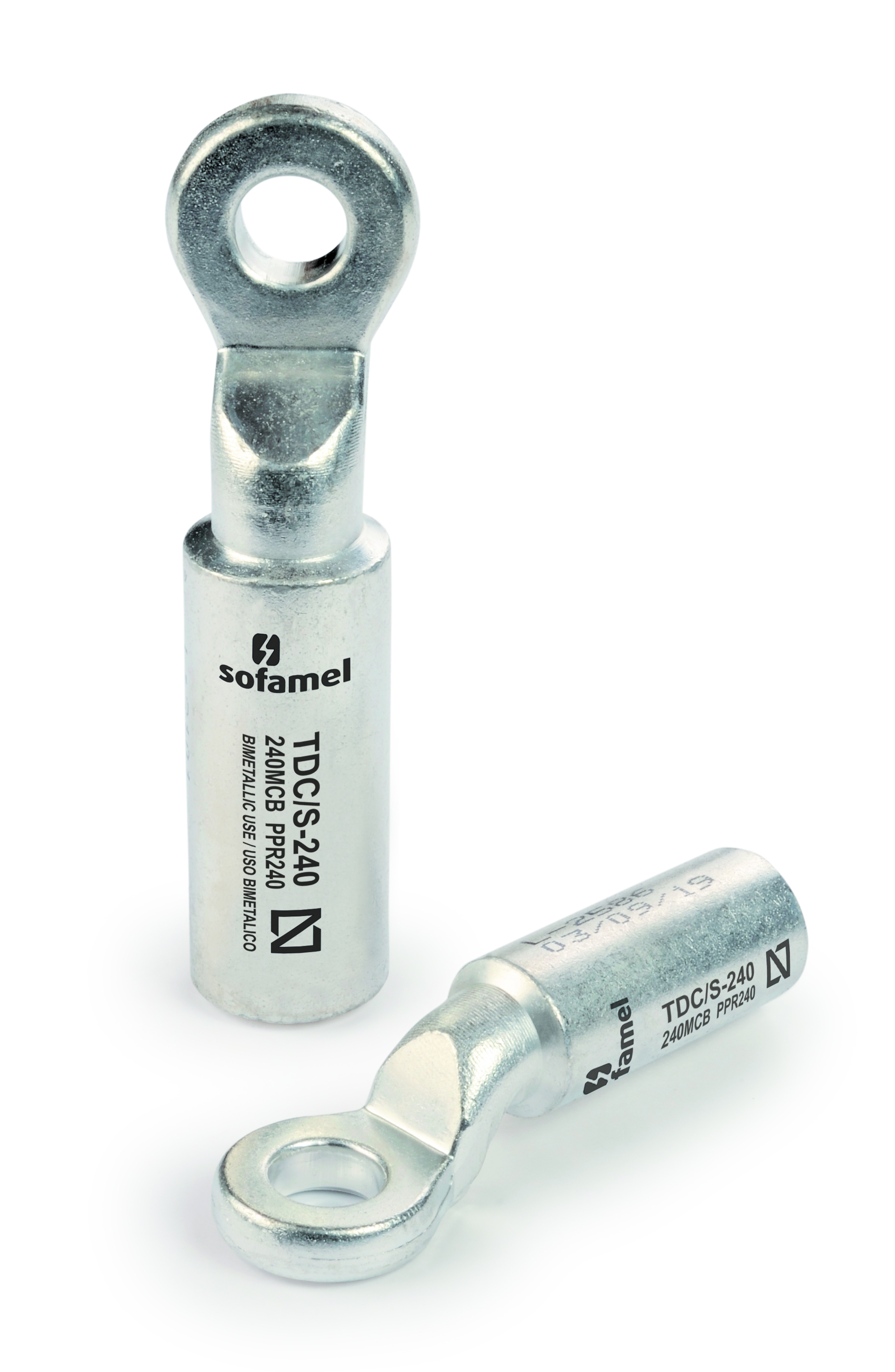
In conclusion, choosing a good electrical connector is essential to ensure the efficiency and safety of electrical installations. Factors such as material, diameter and type of cable and galvanic corrosion must be taken into account when selecting the right connector. Bimetallic connectors are notable for their ability to resist corrosion and their versatility in different applications. Our unique TDC/S terminal is a perfect choice for bimetallic applications as it has a layer of tin. Tin lies between aluminium and copper in the galvanic series and acts as a protective layer between these two metals. Applying a layer of tin by means of an electrolytic bath prevents direct bonding between Al and Cu, thus preventing the chemical reaction. If these aspects are taken into account and quality connectors are chosen, the electrical system is guaranteed to achieve optimum performance and last longer. |


